If you didn't hear about Windows in-built ReadyBoost feature, it's a disk caching software component which enables flash drives and SD cards to act like a memory cache. In most slow performing systems, ReadyBoost improves the overall system performance.
In this article we will learn about ReadyBoost, its minimum requirements and how it works to increase system performance.

What is ReadyBoost?
Along with Windows Vista, Microsoft introduced a disk caching software component which enables USB Flash drives and SD Cards as write cache between your hard disk drive and RAM (Random Access Memory). Using the SuperFetch technology, ReadyBoost increases the computing performance. This caching functionality is available in-built in all Windows Operating Systems, starting Windows Vista.
When you plug-in a compatible device, the Windows AutoPlay dialog offers an additional option to use the flash drive to speed up the system by converting it to use ReadyBoost. It compresses and encrypts all data that is placed on the flash device using AES-128 encryption system.
What are the minimum requirements to use ReadyBoost?
If you would like to use the ReadyBoost to speed up your computer, the following requirements you need to follow:
- The capacity of the device should be at least 256 MB.
- The device must have an access time of 1 ms or less.
- The device should have at least 2.5 MB/s read speeds for 4 KB random reads.
- The device should have at least 1.75 MB/s write speeds for 512 KB random writes.
- The device must be formatted in any of the supported file systems: FAT16, FAT32, NTFS, exFAT.
Does ReadyBoost increase RAM size?
ReadyBoost does not act as a RAM and it will not replace the purpose of RAM. As per the definition of ReadyBoost, it uses SuperFetch technology to cache content to a faster USB or SD Card to provide you better performance. If you think to use it as RAM, you will certainly NOT!
But, if you have a system with less RAM (let's say, around 512 MB), ReadyBoost will improve your overall system performance as it will use faster USB device or SD Card to cache data instead of using slower Hard Disk Drive (HDD). If you are using SSD (Solid State Drive), there's no meaning to use ReadyBoost at all.
Can you use ReadyBoost on Windows 10?
Yes, you can use ReadyBoost in any Windows operating system, starting with Windows Vista. If you are using Windows 10, it might be a perfect solution to use ReadyBoost if your system is slow due to low available memory. If you have a faster USB drive and/or a faster SD Card, you can off-course enable ReadyBoost and check if that gives you a better performance.
How to speed up my computer using ReadyBoost?
If you have a faster Flash drive or SD Card, you can follow the below mentioned steps to enable ReadyBoost, which will give you a kick start to your system:
- Connect a compatible USB drive or a SD Card on your system.
- Open the File Explorer and navigate to 'My Computer' or 'This PC'.
- Right-click on the device and format it to NTFS or exFAT file system.
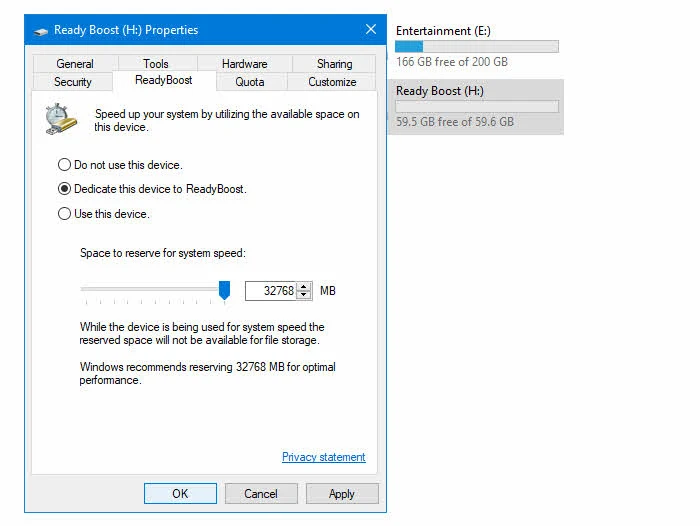
- Once formatting is done, right-click on the device again and navigate to its Properties.
- Under the ReadyBoost tab, either select Dedicate this device to ReadyBoost or Use this device.
- Now drag the slider or enter a value to reserve the space to utilize as ReadyBoost caching.
- Once done, click Apply | OK to save the changes.
- Wait for some time (5-10 minutes) and then restart your system. ReadyBoost will configure the device to use the caching system by creating a disk cache file
ReadyBoost.sfcache in the root directory of the USB drive or the SD Card that you have used.